In most electric boiler installations in a thermal power plant, the available amperage is a major challenge. For industrial installations, the standard is to have a three-phase network with a voltage of 600 V in Canada or 460 V in the United States.
Amperage Calculation
The formula to calculate the amperage in a three-phase circuit is as follows:
Amps (A) = Power (W) / (1.732 x Voltage (V))
For a voltage of 600 V, you can quickly estimate the required amperage based on the power using this simplified formula:
Amps (A) = Power (kW)
For example, for a 100 hp boiler (1000 kW), the required amperage would be 1000 amperes.
Click here to learn more about converting hp to kW.
Infrastructure Challenges
One recurring challenge is the availability of this amperage and the necessary infrastructure to deliver this current to the boiler’s control panel. These constraints often limit the capacity of standard electric boilers in a facility.
Alternatives for Higher Voltages
To overcome these limitations, it is essential to consider higher voltages. In North America, the voltages available beyond 600 V include:
- 4.16 kV
- 6.6 kV
- 14 kV
- 25 kV
The graph below illustrates the relationships between the different voltages, the capacities of the boilers, and the required amperage:
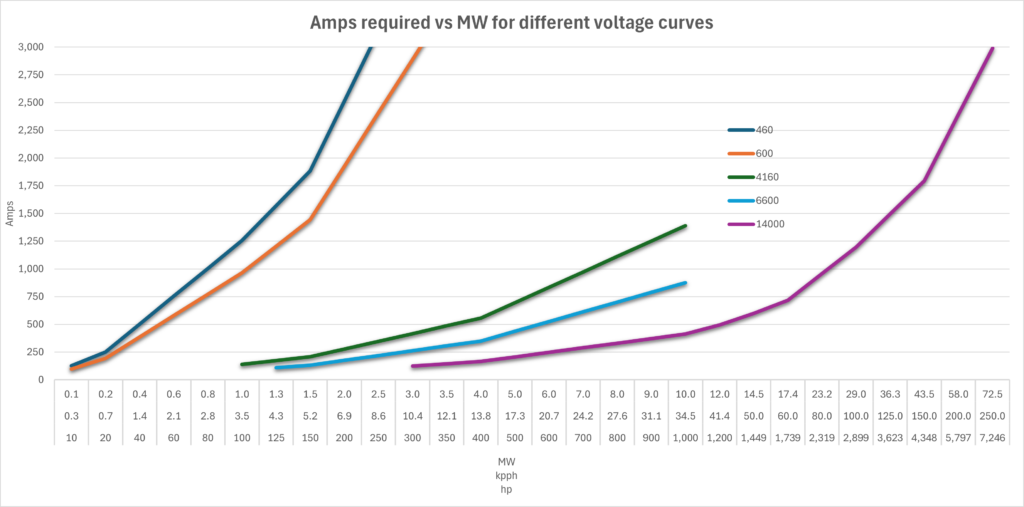
Technologies According to Voltage
Electric boiler technologies vary according to voltage:
- Immersion heater technology (or heating elements) is used in low and medium voltages below 6.6 kV
- Immersed electrode or jet technology is found in voltages above 600 V
For more details, please refer to the technical bulletin on electric boiler technologies.
Additional Resources:
- Technical bulletin on types of electric boilers (coming soon)
- Technical bulletin on the conversion of hp to kW